Diagnosis
In the interest of protecting your health, it’s wise to learn how to give your skin a “safety check” – a periodic examination from head to toe. To start, you should note the size and location of any moles or growths. If one of these growths begins to change or grow rapidly, it’s imperrative to have your dermatologist examine it as soon as possible. Early detection and removal offer the best chance of curing skin cancer.There are three major types of skin cancer: basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma and malignant melanoma.
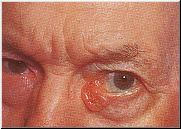
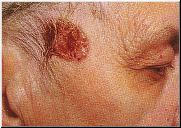
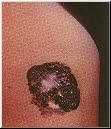
- Basal cell carcinomas (BCC) are raised, translucent, pearly nodules which may crust, ulcerate and sometimes bleed. They occur most often on the face and other exposed areas of the body but can appear in other areas.
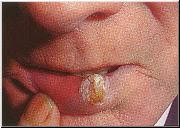
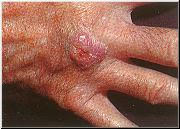
- Squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) are usually raised, pink, opaque nodules or patches which frequently ulcerate in the center. They most often appear on exposed areas of the body but may appear elsewhere.
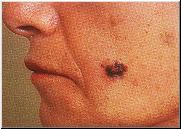
- Malignant melanomas (MM) are usually small, brownish-black or larger multicolored patches, plaques or nodules with irregular outline. They may crust on the surface or bleed. Many of them may arise in preexisting moles.
Treatment
If a skin growth is suspected of being pre-cancerous or cancerous, your dermatologist will usually perform a skin biopsy to confirm the diagnosis. There are many effective treatment options for skin cancer, which include surgical removal, radiation, and chemotherapeutic options. Your dermatologist will provide an appropriate course of treatment based on several factors, ranging from the type and stage of the skin cancer, its location, your overall health, and more.
If many pre-cancers are present, chemotherapeutic creams may supplement treatment. Early detection and removal offer the best chance of curing skin cancer.
- BCC Example 1
- BCC Example 2
Prevention
Sun avoidance is the best way to reduce your risk of skin cancer. While there are other known risk factors such as your heredity, traumatic scarring from disease or burns and exposure to x-rays, overexposure to UV radiation (from the sun or tanning beds), specifically when it leads to sunburn and blistering, is currently thought by medical professionals to be the leading cause of skin cancer.
The important thing to remember is to protect your skin from UV light every day, year-round. The following sun safety tips are based on those provided by the American Academy of Dermatology.
- SCC Example 1
- SCC Example 2
Sun Safety Tips
- Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen (protection from both UVA and UVB rays) with a sun protection factor (SPF) of at least 15 every day
- Don’t forget your lips – apply a lip balm with an SPF 15 or greater
- Reapply sunscreen every two hours when outdoors, even on a cloudy day
- Avoid exposure to the sun’s rays when they are strongest – between 10 a.m. and 4 p.m.
- On average, children get three times more sun exposure than adults. During the summer months, children should wear sunscreens with an SPF 30+
- Babies six months or younger should be kept out of the sun whenever possible
- Wear protective, tightly woven clothing, such as long-sleeved shirts and pants
- Wear a wide-brimmed hat (four inches) and sunglasses when outdoors
- Avoid tanning beds
- MM Example 1
- MM Example 2